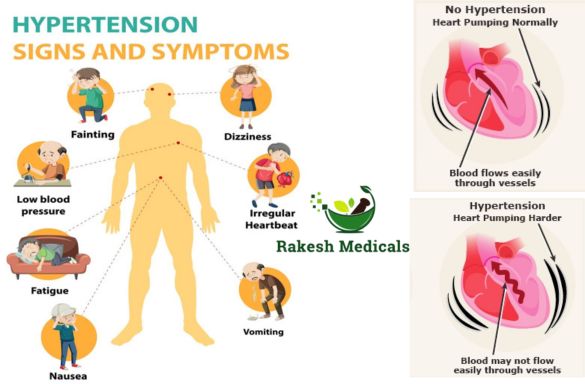
Hypertension, often called the “silent killer,” affects millions globally. According to the World Health Organization, an estimated 1.28 billion adults aged 30-79 have hypertension. This condition can lead to severe health issues, making early detection and management crucial.
Understanding Blood Pressure
Blood pressure measures the force of blood against artery walls. It’s expressed in two numbers: systolic (the pressure when the heart beats) over diastolic (the pressure when the heart rests between beats). For example, a reading of 120/80 mmHg indicates normal blood pressure.
Blood Pressure Ranges
Understanding categories of blood pressure helps identify hypertension stages as defined by reputable organizations like the American Heart Association:
- Normal: Less than 120/80 mmHg
- Elevated: 120-129/<80 mmHg
- Hypertension Stage 1: 130-139/80-89 mmHg
- Hypertension Stage 2: 140 or higher/90 or higher mmHg
Factors affecting blood pressure include age, genetics, lifestyle choices, and underlying health conditions.
Causes and Risk Factors of Hypertension
Primary Hypertension
Primary hypertension is linked to multiple factors without an identifiable cause. It affects nearly 90-95% of people with high blood pressure.
Secondary Hypertension
Secondary hypertension arises from conditions like kidney disease or sleep apnea. For instance, someone with untreated sleep apnea may experience elevated blood pressure due to disrupted sleep patterns.
Lifestyle Risk Factors
Certain lifestyle choices can increase the risk of hypertension:
- Diet: High salt intake elevates blood pressure.
- Physical Activity: Lack of exercise contributes to obesity, a risk factor for hypertension.
- Stress: Chronic stress can negatively influence blood pressure.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive drinking raises blood pressure levels.
- Smoking: Chemicals from tobacco products can damage blood vessels.
Diagnosing and Managing Hypertension
Diagnostic Methods
Blood pressure is typically measured using an inflatable cuff connected to a pressure gauge. Besides this, doctors may recommend blood tests or an ECG for a comprehensive evaluation.
Treatment Strategies
Managing hypertension includes lifestyle modifications and medications:
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Adopt a balanced diet, like the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet.
- Engage in regular physical activity.
- Practice stress management techniques such as yoga or meditation.
- Medications: Various antihypertensive drugs, like diuretics or beta-blockers, may be prescribed. Each class comes with potential side effects, such as dizziness or fatigue.
Regular monitoring is key to managing blood pressure. Frequent doctor visits help track changes and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Complications of Uncontrolled Hypertension
Uncontrolled hypertension can lead to numerous complications:
Cardiovascular Diseases
Hypertension significantly increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and heart failure. Statistics reveal that individuals with hypertension are four times more likely to experience these events compared to those with normal blood pressure.
Kidney Disease
High blood pressure can damage kidneys, leading to chronic kidney disease. Research indicates that approximately 30% of people with high blood pressure also develop kidney issues.
Other Complications
Hypertension can affect other areas, leading to:
- Vision Problems: Damage to the blood vessels in the eyes can impair vision.
- Cognitive Impairment: Research shows a connection between high blood pressure and cognitive decline.
Preventing and Living with Hypertension
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting healthy habits can make a difference:
- Dietary Modifications: Focus on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while reducing salt intake.
- Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly.
- Stress Management: Engage in relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or hobbies you enjoy.
Medication Adherence
Following the prescribed medication regimen is vital. Many struggle with adherence due to side effects or forgetfulness. Finding a routine or using reminders can help.
Support and Resources
Support groups can provide encouragement for those living with hypertension. Websites like the American Heart Association offer valuable resources and guidance.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Blood Pressure
Understanding hypertension is the first step toward managing it effectively. Consistent monitoring and lifestyle choices play a crucial role in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels. Early detection lets individuals lead fulfilling lives while managing this condition successfully. Let’s take charge of our health and work towards a future free from the complications of hypertension.